Last Mile Delivery Metrics: A Comprehensive Overview
Picture this: your customer has bought that new, shiny product they’ve had on their wishlist for a while. The credit card details are in, the invoice has been sent, and the product has been picked, packed, and shipped. The only thing left to do now is wait for that package to get delivered to your customer’s doorstep. We’re in the last-mile delivery stage of your customer’s order, and it’s here where things can go wrong.
Keeping track of last-mile delivery operations is a crucial metric to ensure the success of a logistics business. A seamless delivery generates repeat customers happy with their purchase, whereas failed deliveries are a missed opportunity to enhance customer experience.
But how exactly can a business keep on top of its last-mile delivery metrics? What kind of metrics should logistics service providers track, and how can they use this data to improve last-mile delivery performance? This comprehensive guide will cover all this and more.
Section 1: Understanding Last-Mile Delivery Metrics

Last-mile delivery metrics encompass measurements that focus on the final part of the delivery process, from the warehouse or distribution center to the customer’s home or business location. The data collected from these measurements are then used to implement systems to improve order accuracy and operational efficiency.
While each business may choose to record and monitor different metrics, some common key performance indicators (KPIs) used include on-time delivery rates, average delivery time, average delivery distance, customer feedback scores (and customer complaints, including damage complaints), fuel consumption rates, and the percentage of completed deliveries within specified time windows.
Key Metrics Explained

While last-mile logistics companies may focus on different metrics, some last-mile KPIs are especially important. These include:
- Average Delivery Times – The complete duration it takes for packages to be transported from the warehouse to their destination. This is important to ensure speedy deliveries and a rapid average service time so that the customer receives their products promptly.
- Cost Per Delivery – Thie expenses incurred for each individual delivery, including factors like fuel costs, labor, vehicle maintenance, and any operational overheads. This metric is vital to ensure that profits are maximized and that the real delivery costs are calculated to cover expenditure.
- Success Rate – The percentage of deliveries that are completed successfully without any issues or delays, a number critical for customer satisfaction rates.
- Customer Satisfaction – How happy customers are with the delivery process. Satisfaction could include low numbers of damage claims, on-time deliveries, and a general feeling about customer service provided.
These four metrics provide the basis of many companies’ last-mile delivery KPIs as they cover all key elements of running a business: customer satisfaction, performance, and costs.
Benefits of Monitoring and Analyzing Metrics
While measuring metrics can be a challenging business process to implement consistently, it’s important that logistic companies track such metrics to improve their performance and operational efficiency. Last-mile delivery metrics that are tracked accurately can improve resource allocation, reducing costs and wasted labor time. In addition, last-mile delivery KPIs are useful tools to improve decision-making, enhance customer satisfaction rates, and optimize processes and routes.
Section 2: Challenges in Implementing Last-Mile Delivery Metrics
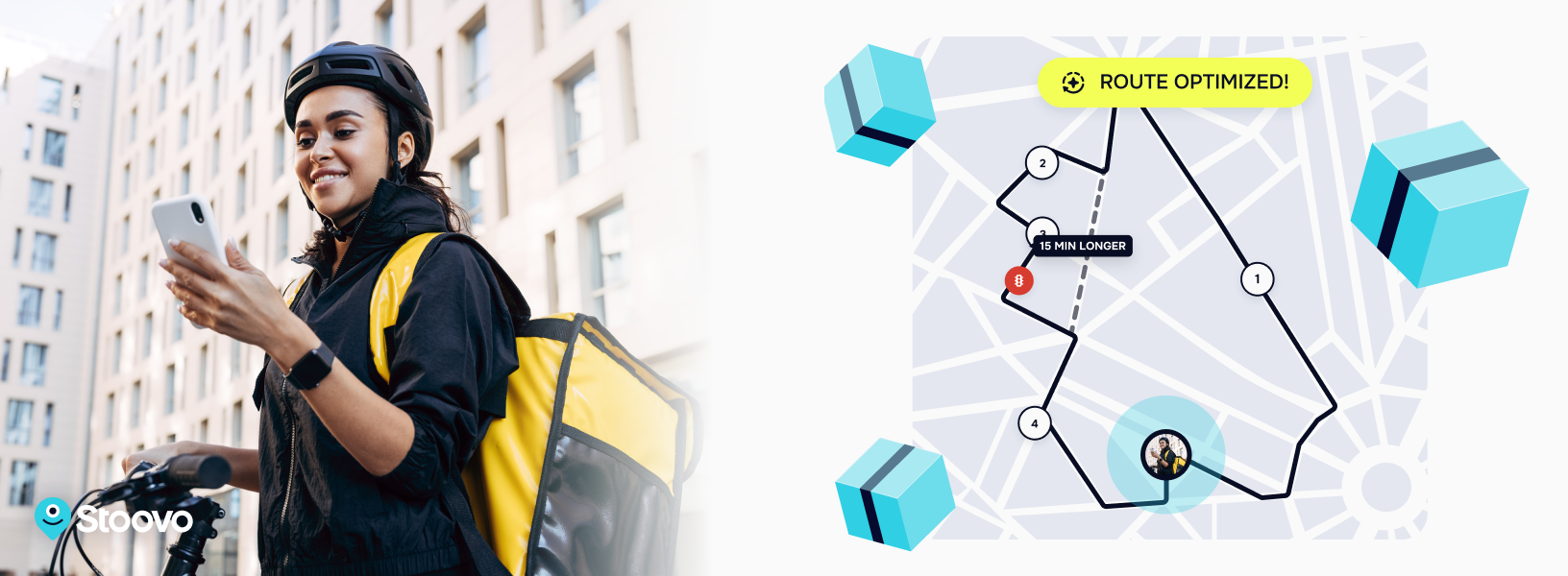
Although important, last-mile delivery metrics are not always simple to track and measure. Problems arise when implementing data collection processes.
There are numerous challenges when implementing last-mile delivery operations – including performing time-pressured deliveries – and so-the-ground team members may push back at being asked to monitor their delivery schedules to accommodate real-time tracking and data recording. Moreover, any data collected must be in appropriate formats to integrate seamlessly with existing delivery business software, including business insight software, HR and scheduling tools, and ERP software in use. The ideal last-mile delivery solution is easy to use, tracks data automatically, and integrates precisely – which proves to be an elusive combination.
Even when the data is tracked and allocated correctly into the system, more is needed to ensure that the data is accurate and reliable. Should inaccurate data find its way into the decision-making process, route optimization [link to dynamic route optimization blog] may mean route de-optimization, with decisions made which negatively impact the business overall.
Fundamentally, and the most prominent challenge with implementing any data strategy, metrics collected are only as good as the use businesses get from them. More than simply collecting data is required; rather, having a strategy to align metrics with business goals, optimize routes, and improve operational efficiency should be the target of last-mile delivery operations – not simply collecting data for data’s sake.
Section 3: Strategies for Optimization

How can businesses then overcome these challenges to leverage strategies for harnessing data? What key strategies can last-mile delivery partners use to get the most out of the metrics they track and see a return on their investment?
Strategy One: Leveraging Technology and Automation
Firstly, an essential strategy for businesses is to tap into emerging technologies and the benefits of automation in the last-mile delivery process.
Emerging apps using real-time data make deliveries easier. Take Stoovo, as an example, which serves as an AI-powered navigation app designed specifically for last-mile delivery drivers. Stoovo provides relevant, up-to-the-minute destination information to optimize efficiency and minimize potential delays and is easy to download and use – meaning limited driver training time is needed. Apps like Stoovo can automatically calculate the best route for a driver to take based, helping drivers push up their KPIs and increase their on-time delivery rate.
It’s not just new apps that appeal. Increased automation and the use of AI predictive tools can help businesses predict delays and disruptions based on historical data. For instance, an AI model could predict what roads tend to get congested at which times and re-route drivers to avoid them. This brings average delivery times down and improves the fleet’s fuel consumption rate by avoiding idle times in traffic. Perhaps even more exciting is that automated route planning software can do this automatically – with limited need for human involvement. By reducing labor expenditure and decreasing average delivery costs, businesses don’t need to wait long to see their investment pay off.
Strategy Two: Tailoring Metrics to Specific Business Needs
Secondly, delivery metrics are not a one-size-fits-all strategy. Although many businesses track the top four metrics – on-time deliveries, delivery accuracy, first-attempt delivery success, and customer satisfaction – last-mile logistics companies should not see this as an exhaustive list. Instead, it may be better to track overlooked metrics such as actual mileage vs. planned mileage, empty miles vs. vehicle capacity usage, delivery efficiency, and overall vehicle costs.
It’s critical that unique businesses tailor their tracking and metrics to their specific business needs. This means working towards a goal and then finding and tracking the correct metrics to help achieve it. From route optimization to reducing damage claims, decreasing cost per mile to increasing the use of electric vehicles in a green strategy, metrics should be chosen carefully to assist businesses in reaching their goals.
Strategy Three: Continuous Monitoring and Improvement Strategies
Business leaders can often pull up key metrics on demand, but having the data in front of your decision-makers is only half the battle. The final step towards optimization is putting in place systems to use that data to make decisions and improve organizational efficiency.
Doing so involves the continual monitoring of a comprehensive data strategy that may evolve over time. It also involves building a data analysis team with the power to make decisions. Finally, increasing improvement requires a cultural shift, paying attention to the recommendations of analysts and taking their recommendations seriously by implementing them.
Section 4: How Amazon Uses Last Mile Metrics
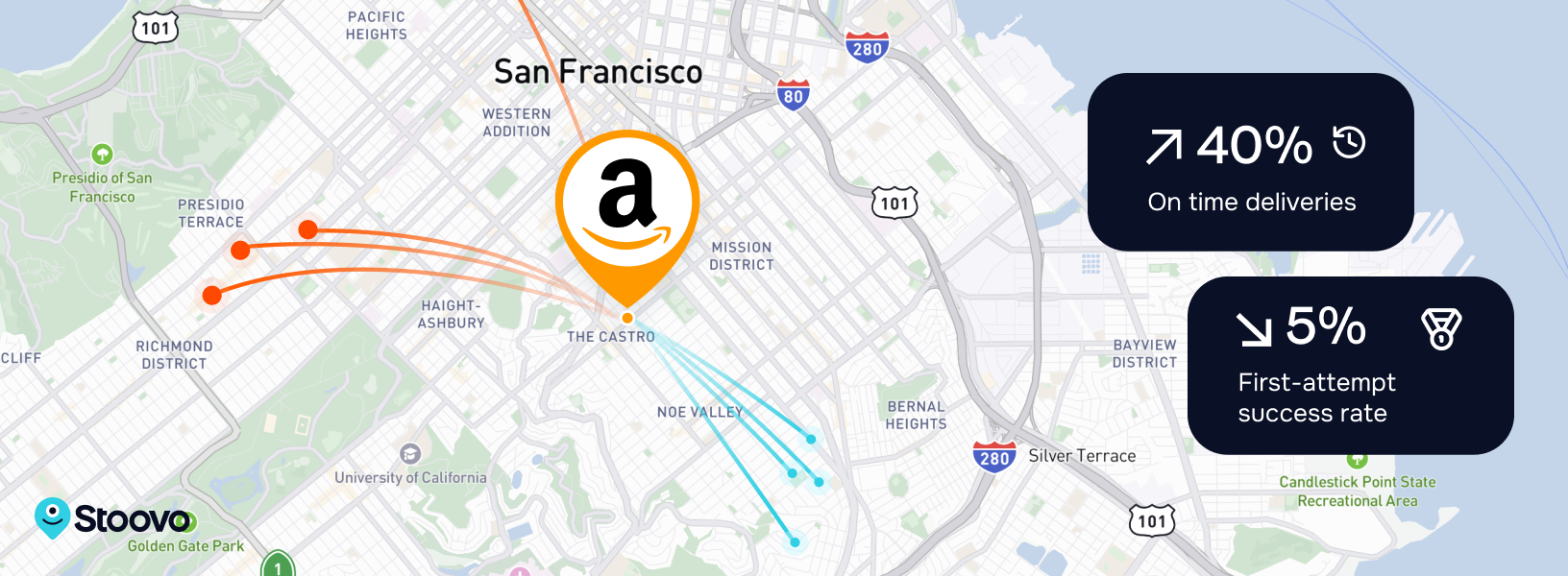
When looking at the delivery industry, the behemoth Amazon is a clear industry leader. Behind their success is a wealth of last-mile data that inform their strategy.
Amazon examines traditional last-mile metrics and harnesses dynamic routing to plan shipping routes and delivery schedules while accounting for traffic flow, road closures, and other variables affecting delivery time. Amazon’s proprietary route optimization software then uses this data to optimize routes, ensuring swift and efficient package deliveries by utilizing advanced algorithms to select the quickest paths for each delivery and adapting timeframes based on traffic and weather circumstances.
But Amazon doesn’t stop there. In optimizing its last-mile delivery service, Amazon’s data analytics go all the way back to the demand side. Amazon examines customer behavior and preferences before the product has been purchased. Then, by analyzing customer order data, the system can anticipate high-demand products and their potential ordering locations through AI-driven user recommendations. This approach facilitates stocking popular items strategically in nearby warehouses and pre-allocating load space within the fleet, ultimately reducing delivery times and optimizing the last-mile process.
Data analytics thus plays a pivotal role in Amazon’s success. Through analyzing extensive data captured on customer behavior, shipping paths, inventory control, and delivery outcomes, Amazon has enhanced its delivery procedures from the time the customer thinks about ordering something right the way through to their last mile obligations. As a result, Amazon can guarantee swift and streamlined package deliveries and sets the standard for last-mile logistics.
Section 5: Future Trends and Innovations
So, where does the industry go from here? With industry leaders such as Amazon setting the standard for delivery speed and customer experience, have we reached the pinnacle of last-mile logistics?
The experts say no. There are still exciting developments on the horizon that may yet change the way last-mile delivery companies perform, and as consumers, we may benefit even more from enhanced last-mile services.
Emerging Technologies in Last Mile Delivery
The technological field is still advancing, and with radically more data available, last-mile logistics are set to improve. Massive data-sharing applications, like Stoovo, have the ability to enhance last-mile deliveries for drivers, giving real-time information that makes a crucial difference. Plus, recent experiments with drones and autonomous driving could provide even more opportunities for optimization, working 24 hours to rapidly and safely bring consumers the goods they desire immediately.
The Role of Big Data and Analytics
All the key ways of measuring last-mile deliveries rely on one thing – data. And with the proliferation of big data, it’s inevitable that deliveries will improve. As humans rely more and more on data, there will be even more data on which to base decisions, meaning metrics become more accurate and reliable. Optimizing for the right metrics will no longer be a challenge, and businesses will have immeasurably more information at their fingertips on which to make decisions.
Sustainability Considerations
As we enter into a period of global heating, the pressure is on businesses to reduce the actual mileage for each delivery and use their resources sustainably. In the future, logistic companies will be required to overcome increasing consumer and regulatory pressure to reduce emissions, and optimizing last-mile delivery processes is a key way of doing so. In addition, as fuel prices rise and margins are squeezed, the whole supply chain will feel the effects, meaning sustainability and reducing costs will be critical drivers of last-mile efficiency.
Final Thoughts

Last-mile delivery metrics are not just figures and statistics on a screen or another arduous task added to a delivery driver’s to-do list. Instead, these metrics represent the workings of an efficient, customer-centric supply chain, improving speed and delivering better customer satisfaction outcomes.
By tracking and analyzing metrics such as on-time deliveries, first-attempt success rates, and customer satisfaction, last-mile delivery businesses can fine-tune their operations to meet rising expectations for rapid, reliable deliveries.
Looking ahead, as technology, including AI and autonomous vehicles, continues to evolve, the increased integration of real-time Big Data, AI-driven route optimization, and predictive analytics will completely reshape the landscape of last-mile delivery. Through industry behemoths such as Amazon, we can see the importance of last-mile delivery metrics in getting ahead of the competition and delivering more reliable customer service.
Ultimately, it is paramount for logistics companies to embrace advancements in last-minute metrics and embed the collection and prioritization of data into their last-mile workflows. Businesses must embrace this new technology to ensure they stay competitive and consistently deliver excellent customer service.
FAQs
What are key performance indicators for delivery?
There are many KPIs that can be used for delivery, including metrics such as on-time delivery, delivery accuracy, route efficiency, fuel costs, customer satisfaction rates, and cost per delivery. These metrics collectively reflect the effectiveness of the delivery process and identify space for improvement.
What are the four metrics of delivery performance?
The four metrics of delivery performance often include on-time deliveries, delivery accuracy, first-attempt delivery success, and customer satisfaction. However, this is not an exhaustive list and last-mile delivery metrics could include many other key performance indicators.
What is KPI in logistics?
KPI in logistics stands for Key Performance Indicator, which is a metric or target used to assess the performance of operations within a logistics company. KPIs are crucial measures of success and failure within the business and help an organization meet its strategic goals.